Definition of IT Cloud
IT Cloud refers to a network of remote servers that are hosted on the internet, and it allows users to store, manage, and process their data over a secure internet connection. The cloud computing model delivers different services such as Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), among others.
Table of Contents
The Importance of IT Cloud in Modern Businesses
IT Cloud is essential for modern businesses because it provides an array of benefits. Firstly, it allows companies to cut costs associated with purchasing hardware infrastructure for data storage and management.
Instead of building an expensive onsite server room with support staff, companies can use cloud services offered by providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). This saves them time and money while providing unmatched flexibility in scaling up or down their needs.
Secondly, using IT Cloud enables companies to access their data from anywhere at any time without worrying about security or technical issues. This flexibility ensures that employees can work remotely from anywhere around the world without compromising productivity or security.
Thirdly, It provides better collaboration channels for teams working together on projects across different locations globally. Sharing files between team members has never been easier than with cloud-based tools like Google Drive or Office 365 SharePoint Online.
These solutions allow coworkers to work together seamlessly regardless of where they are located. Fourthly, using IT cloud services also ensures disaster recovery and business continuity because data is backed up automatically in multiple locations.
This guarantees that in case of a system crash, power outage, or natural disaster, companies can quickly restore their data without significant losses. IT Cloud allows businesses to remain agile and competitive by providing state-of-the-art resources to keep up with the latest technological trends.
By working with cloud providers who offer services such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, and edge computing solutions, companies can leverage these technologies to build better products and services. IT Cloud is vital for modern businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve.
Its cost-effectiveness, flexibility in scaling up or down needs and better collaboration channels are some of the reasons why many companies have adopted it as an integral part of their operations. Its importance continues to grow as more organizations seek new ways to leverage technology for competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
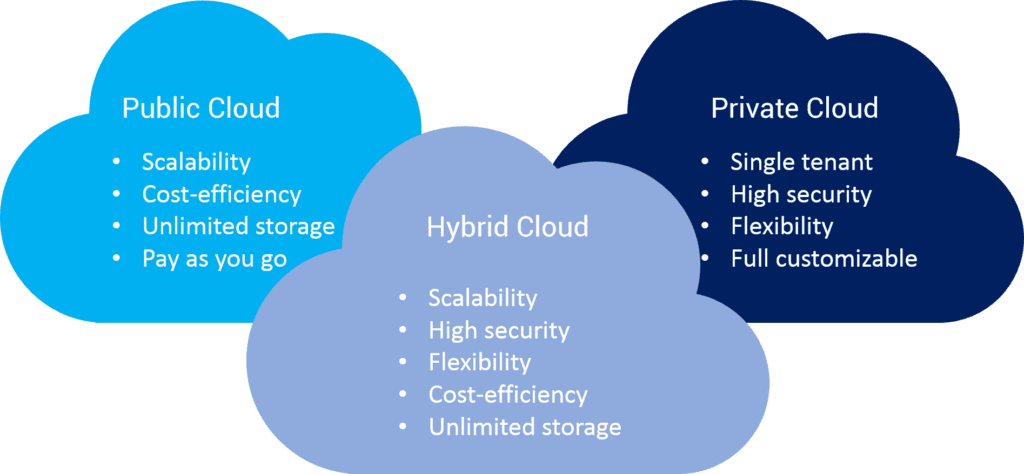
Types of IT Cloud
The cloud has become the heart of digital transformation and innovation for businesses. A recent survey by RightScale found that 96% of respondents use cloud technology, with more than 80% using a multi-cloud approach by adopting a combination of public, private, and hybrid clouds to meet their business needs.
Public Cloud
A public cloud is a type of IT cloud in which services and infrastructure are provided off-site over the Internet by third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform or Microsoft Azure.
Public clouds offer several benefits such as reduced upfront costs, no maintenance fees or overheads, quick deployment, flexibility and scalability. Public clouds are most suitable for businesses that require high compute power but do not have the necessary resources to maintain an in-house infrastructure.
Public clouds are ideal for startups who require access to advanced computing facilities at affordable prices. They also work well for companies operating in industries that do not deal with sensitive data.
However, there are downsides to public clouds too. The biggest concern is data security since third-party providers have access to your sensitive data as it resides on their servers.
Additionally, organizations can face compliance issues because they have limited control over where their data is stored and who has access to it. Despite these concerns, public clouds remain a popular choice among businesses because they offer low-cost computing solutions coupled with ease-of-use.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is an IT cloud infrastructure provisioned specifically for one organization’s use either on-premises or within a service provider’s data center. Private clouds offer greater control over security measures and provide dedicated resources for a business, ensuring that the cloud infrastructure can meet the company’s specific requirements.
By leveraging a private cloud, businesses can enjoy increased privacy and control over their data. Private clouds are suitable for businesses that require high levels of security, compliance or data privacy, such as law firms or healthcare providers.
They work best in industries where regulatory compliance is strictly enforced and where companies need to ensure their data remains within a specific geographic location. However, maintaining an onsite private cloud requires significant investment in hardware, software and skilled staff.
Also, the cost of setting up a private cloud infrastructure may outweigh any benefits gained from having dedicated resources. Despite these challenges, private clouds remain popular among large businesses due to enhanced security measures and greater control over compute resources.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is an IT solution which combines the features of both public and private clouds. This type of IT cloud allows businesses to take advantage of the scalability and flexibility of public clouds while maintaining control over sensitive data in a private cloud environment.
The hybrid approach uses a combination of on-premises infrastructure with public or third-party provider services to provide additional computing power when required. Hybrid clouds allow companies to maintain complete control over their critical applications and sensitive data while harnessing the benefits provided by public clouds such as scalability and cost savings.
The hybrid model is suitable for organizations who have legacy systems that cannot be migrated immediately but want to take advantage of new technologies like big data analytics via services like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure. With the help of hybrid architectures, companies can continue using tried-and-tested traditional IT solutions while integrating new technological advancements as they come along without significant disruption to operations.
All three types of IT cloud have their own advantages and disadvantages. The suitability of each type for a particular business depends on factors such as the size of the organization, its security needs and compliance requirements.
A public cloud infrastructure is ideal for small businesses that require cost-effective computing resources whereas a private cloud offers better control over data security and privacy, although it requires significant investment. Hybrid clouds are increasingly popular due to the ability to combine the benefits of both public and private clouds while maintaining control over critical applications or data.
Benefits of IT Cloud
The adoption of cloud computing has brought about a wide range of benefits to businesses, both small and large. Some of the outstanding benefits include cost savings, scalability and flexibility, disaster recovery and business continuity, as well as increased collaboration and productivity.
Cost Savings
One major benefit of IT Cloud is cost savings. This is because it eliminates the need for businesses to invest in expensive physical infrastructure such as servers, storage devices, and network equipment.
Instead, cloud providers offer a wide range of services that can be paid for on-demand basis or through subscription models. This helps businesses save costs on hardware purchases, maintenance costs, energy consumption costs, and other overheads associated with physical infrastructure.
In addition to this, cloud computing providers usually offer economies of scale benefits due to their massive infrastructure investments. This means that businesses can leverage the provider’s economies of scale to access high-quality services at lower costs than they could procure independently.
Scalability and Flexibility
IT Cloud also provides scalability and flexibility benefits that are crucial in today’s fast-paced business environments. With cloud computing services such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), or Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), businesses can easily scale their operations up or down based on their needs. This means that companies no longer have to worry about investing in costly hardware upgrades or adding new servers each time they need more capacity.
Instead, they can simply request additional resources from their service provider who will then allocate them within minutes. Furthermore, IT Cloud also offers great flexibility since employees can access cloud services from anywhere using any device with an internet connection which is vital in today’s remote work environment.
Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity
Cloud computing also provides disaster recovery and business continuity benefits by offering reliable backup and storage services. With cloud-based disaster recovery solutions, businesses can easily access their data and applications in the event of a disruption caused by natural disasters, cyber-attacks or any other unexpected events. This means that businesses can quickly recover from disasters with minimal downtime and without losing important data.
Additionally, most cloud providers offer geographically dispersed data centers that provide redundancy and failover capabilities. This ensures that if one data center goes down, the business operations can continue from another location.
Increased Collaboration & Productivity
IT Cloud also promotes increased collaboration and productivity among employees through various collaborative tools such as video conferencing, instant messaging, file sharing, and project management software. These tools help teams work more efficiently regardless of their physical location or time zone. Moreover, cloud computing allows employees to access their work files remotely from anywhere at any time which further enhances productivity by enabling them to work on-the-go.
The benefits of IT Cloud are numerous including cost savings, scalability and flexibility, disaster recovery and business continuity as well as increased collaboration and productivity. By leveraging these benefits through careful planning and implementation of IT Cloud solutions companies can gain a competitive edge in today’s ever-evolving business landscape.
Challenges of IT Cloud
Security Concerns
One of the biggest challenges associated with IT cloud is security. When data is uploaded into a cloud platform, it is no longer on the company’s own servers. This means that companies are entrusting sensitive data such as financial records, employee information, and intellectual property to third-party vendors.
As a result, security breaches have become frequent occurrences in recent years. In order to mitigate these security risks, companies should ensure that they select reputable cloud providers who demonstrate a strong track record of security and compliance issues.
Additionally, access controls should be put in place to restrict access to sensitive data only to those who need it. Encryption should also be used to protect data while it is being transmitted over the internet.
Data Privacy Issues
Data privacy issues are another major challenge associated with IT cloud. Companies risk losing control over their data once it leaves their own servers and enters the cloud environment. This can lead to breaches of confidentiality or theft of sensitive information by cybercriminals.
To address these concerns, companies must ensure that they understand where their data is stored and how it is being protected at all times. They must also ensure that their cloud provider has implemented appropriate measures for data protection such as secure encryption techniques and regular system audits.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Another challenge for businesses moving towards IT cloud includes integrating legacy systems into new infrastructure environments seamlessly. Many enterprises have spent significant amounts of money developing custom applications which are critical for delivering core business services.
The integration process can be challenging because legacy systems may not be compatible with newer technologies or platforms used in the cloud environment. Enterprises must carefully consider how they will integrate legacy systems into new infrastructure environments without disrupting operations or compromising security.
While IT Cloud offers several benefits, there are also significant challenges associated with it such as security, data privacy issues, and integration with legacy systems. It is important for businesses to carefully consider these challenges before migrating to the cloud and put strategies in place to address them in order to reap the full benefits of cloud computing.
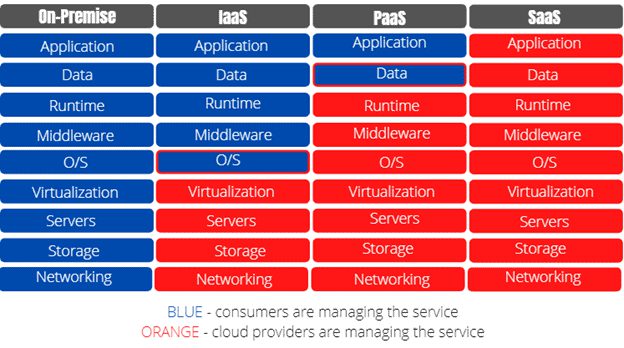
Applications of IT Cloud
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
When it comes to building and managing an IT infrastructure, IaaS is the most popular cloud service model. IaaS provides businesses with basic computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking components on a pay-as-you-use basis. This means that businesses can scale their infrastructure up or down based on their current needs without having to worry about investing in costly hardware that may end up being underutilized.
One of the main advantages of IaaS is that it allows businesses to have complete control over their infrastructure while offloading the burden of maintaining and upgrading physical hardware. This makes IaaS ideal for organizations with dynamic or unpredictable workloads that require frequent scaling up or down.
Some common examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Each provider offers various benefits such as cost-effectiveness, high availability, security features, geographic diversity amongst others.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is another popular cloud computing platform service model that offers developers a complete environment for building, testing and deploying applications within the cloud ecosystem. PaaS typically includes operating systems, middleware services such as databases or message queues, development tools like integrated development environments (IDEs) and other application-specific features.
PaaS eliminates the need for businesses to invest in expensive hardware or software licenses required for developing applications in-house. Developers can focus on writing code without worrying about infrastructure management concerns such as load balancing or server maintenance.
Like with other cloud models PaaS also enables scalability: developers can easily add more resources when demand increases which helps maintain optimal performance levels. Examples of PaaS providers include Heroku by Salesforce.com, Google App Engine and Microsoft Azure App Service.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a cloud computing service model that delivers software applications over the internet. Businesses can access SaaS applications through a web browser or an application programming interface (API).
One of the key benefits of SaaS is its ease of use. The SaaS provider handles all the maintenance, upgrades, and security patches, making it easier for businesses to stay up-to-date with the latest software versions without having to worry about compatibility or installation issues.
Examples of popular SaaS providers include Microsoft 365, Salesforce.com, Dropbox, Slack and Google Workspace (formerly known as G Suite). These providers offer a wide range of services including CRM tools, file storage and sharing platforms, team collaboration software amongst other solutions.
Comparison between IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
To better understand which cloud service model suits your needs best here’s a quick comparison between IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Iaas: gives complete control over infrastructure; requires more management overhead
PaaS: ideal for developers; provides pre-built environment to build apps; less management overhead than Iaas SaaS: ideal for end-users with no upfront costs; pay-as-you-use pricing model.
Cloud computing has become an essential part of modern businesses today providing numerous benefits like cost savings on infrastructure management and scalability among others. Infrastructures as a Service (Iaas), Platform as a Service (Paas) and Software as a Service (Saas) are three main categories under which most cloud-based services fall into.
It’s important to note that each category has its advantages depending on what your business needs are. Whether you’re looking for complete control over your infrastructure or want to offload most responsibilities onto vendors by adopting PaaC or Saas models there’s a lot to choose from in today’s increasingly competitive environment.
Future Trends in IT Cloud
As technology continues to advance, the future of cloud computing appears to be heading towards more advanced and sophisticated solutions. Among the most significant trends that we can expect to see in the near future are edge computing and IoT integration, as well as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in cloud computing.
Edge Computing and IoT Integration
One of the ways that cloud computing is evolving is through edge computing, which brings computation and data storage closer to where it’s needed. Edge computing allows businesses to reduce latency by processing data closer to where it was generated.
This can improve response times for real-time applications, such as those used in manufacturing or autonomous vehicles. In addition, we can expect to see more widespread integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) with cloud computing.
The IoT involves connecting devices such as sensors, cameras, and other machines to a network so they can communicate with each other. By integrating these devices with cloud technology, businesses can leverage real-time data analyses for better decision-making.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cloud Computing
Another trend that is gaining momentum in the world of cloud computing is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies are already being used in various industries such as healthcare, finance, marketing, etc., but their impact on cloud technology will be tremendous. For example, AI algorithms could help optimize workloads by analyzing usage patterns and predicting future demand.
ML could help detect anomalies or potential security threats before they become major issues by monitoring all aspects of a business’s network traffic simultaneously. Moreover, AI platforms will continue evolving to offer more robust solutions for natural language processing (NLP), speech recognition, image recognition/processing etc., using deep neural networks coupled with GPU-accelerated hardware infrastructure.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite the numerous benefits and opportunities that come with cloud computing, there are still some challenges to overcome. One of the biggest challenges is data privacy and security concerns.
As businesses continue to move sensitive data to the cloud, they need assurance that their data will remain secure and protected from unauthorized access. Another challenge is integration with legacy systems.
Legacy systems tend to be complex and difficult to migrate, which can make it challenging for businesses to fully harness the power of cloud computing. Businesses must also consider network bandwidth limitations when migrating to cloud environments as this may limit their ability for real-time decision-making.
Case studies on successful implementation of IT cloud in businesses
Several businesses have successfully implemented IT cloud solutions into their operations resulting in significant benefits. For example, Netflix uses IT cloud services to provide seamless streaming of its content to millions of users worldwide. Another example is Airbnb which uses IT cloud services to manage bookings, communications, and payment processing for its worldwide network of hosts and guests.
The Netflix Case Study – Scaling with the Cloud
Netflix, a leading global provider of streaming entertainment services, has been utilizing the cloud for over a decade. The company transitioned from its own data centers to Amazon Web Services (AWS) in order to scale rapidly and efficiently.
With AWS, Netflix has been able to optimize its infrastructure for high availability and performance while ensuring that its media assets are secure and available anywhere in the world. Furthermore, they use machine learning algorithms in their cloud computing environment to recommend content and personalize user experience based on viewing history.
The Philips Case Study – Improving Healthcare Services with the Cloud
Philips is a well-known healthcare technology company that leverages cloud computing to improve patient outcomes by providing clinicians with access to real-time patient data. Philips has developed HealthSuite Digital Platform which provides clinicians with data analytics tools for risk stratification, medical equipment management, remote monitoring, and more. This platform enables healthcare providers to deliver personalized care that is tailored to patients’ needs based on data-driven insights.
The Lyft Case Study – Reducing Costs with the Cloud
Lyft is an on-demand transportation company that matches drivers with passengers through its mobile application. The company has reduced costs by using AWS as its primary infrastructure provider. By leveraging AWS’s auto-scaling capabilities and pay-per-use model, Lyft has been able to reduce operational costs while scaling quickly during peak hours.
The Capital One Case Study – Enhancing Security with the Cloud
Capital One is one of the largest banks in North America that uses cloud-based security solutions to protect sensitive information such as customers’ financial records and transaction history. Capital One’s Critical Cybersecurity Controls (C3) program aims at providing continuous monitoring of applications hosted within their cloud environment which helps them in identifying and mitigating cybersecurity risks. By leveraging cloud technologies, Capital One has been able to increase its agility and improve security posture.
The Coca-Cola Case Study – Innovating with the Cloud
Coca-Cola Enterprises (CCE) is one of the largest beverage bottling companies in the world that has embraced cloud computing to drive innovation. With the help of Microsoft Azure, CCE launched a new mobile application that gave consumers access to personalized offers, rewards, and promotional campaigns. The app was able to collect user data which helped CCE in understanding customer preferences, and this provided important insights into how they could tailor their marketing strategies.
These case studies demonstrate that cloud computing can be a game-changer for businesses across various industries. By leveraging cloud infrastructures, organizations can scale their operations quickly while reducing costs associated with maintaining physical IT infrastructure on-premises.
Furthermore, cloud-based solutions provide enhanced security measures which are crucial for protecting sensitive data such as financial records or personal health information. Cloud technologies enable businesses to innovate faster than ever before by providing access to cutting-edge tools such as machine learning algorithms and real-time data analytics dashboards.
Cloud computing has become an essential component for many businesses today, enabling them to reduce costs and increase efficiency. However, as technology continues evolving rapidly, we can expect new trends such as edge computing and IoT integration, along with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in the near future.
As these advancements take hold, significant challenges remain such as those regarding security concerns and legacy system integration. Nonetheless, with greater awareness of these issues among business leaders coupled with better technological solutions on horizon provides great promise towards reaping rewards of Cloud Computing in all industries alike while staying ahead of competition through innovation in this realm.